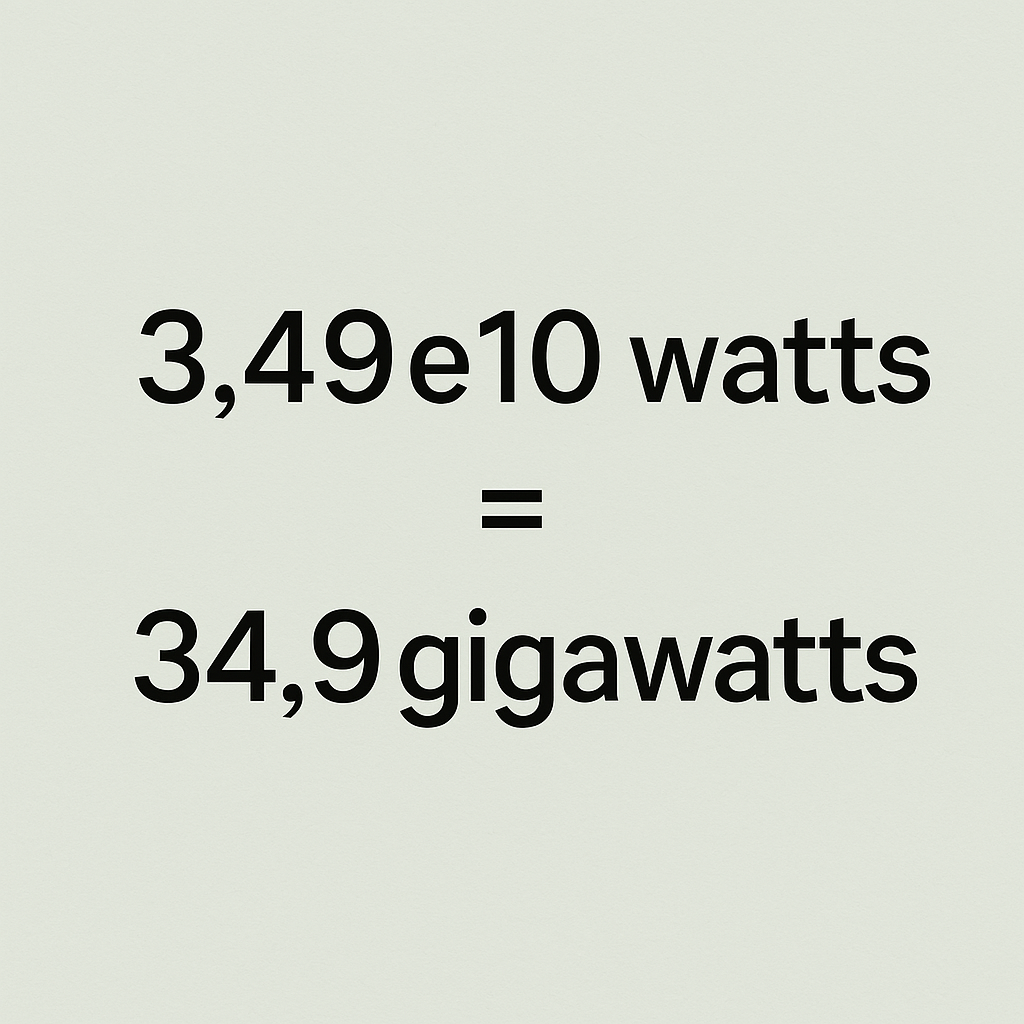In today’s modern, energy-conscious world, the ability to convert units of power accurately is vital for scientists, engineers, students, and anyone working with large-scale electrical systems. One of the most common conversions you might encounter in technical documents, energy production reports, or physics problems is converting watts (W) to gigawatts (GW). In this article, we will break down the process of converting 3.49e10 watts to gigawatts, explore what the values represent, understand their significance in real-world applications, and offer a deeper dive into energy metrics and systems.
What is a Watt?
A watt is the SI (International System of Units) unit of power. Power, in this context, refers to the rate at which energy is used or generated. One watt is equivalent to one joule of energy per second.
The unit is named after James Watt, the 18th-century Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer, who made fundamental improvements to the steam engine and paved the way for the Industrial Revolution.
In simple terms:
-
1 watt (W) = 1 joule/second
Watts are used to measure everything from the power of a small LED light bulb (like 5W) to large industrial machines or data centers consuming megawatts or even gigawatts of power.
Scaling Up: From Watts to Gigawatts
As technology advances, so does the scale of energy consumption and production. While watts might be useful for home appliances or electronics, large power stations, industrial processes, and global energy metrics often use larger units, such as:
-
Kilowatts (kW) = 10310^3 watts
-
Megawatts (MW) = 10610^6 watts
-
Gigawatts (GW) = 10910^9 watts
-
Terawatts (TW) = 101210^{12} watts
So, when we’re dealing with huge numbers like 3.49e10 watts, it’s practical to convert that into gigawatts to make it more readable and understandable.
Breaking Down 3.49e10 Watts
The number 3.49e10 is written in scientific notation, which is a way of expressing very large or very small numbers succinctly. Here’s how to interpret it:
-
3.49e10 watts = 3.49 × 10^10 watts = 34,900,000,000 watts
To convert this to gigawatts, we divide by 10910^9:
3.49×1010109=34.9 gigawatts\frac{3.49 \times 10^{10}}{10^9} = 34.9 \text{ gigawatts}
✅ Final Answer: 34.9 Gigawatts
This means that 3.49e10 watts is equivalent to 34.9 gigawatts.
Understanding the Magnitude of 34.9 Gigawatts
So, what does 34.9 gigawatts actually mean in real-world terms? It’s an immense amount of power. To give you some perspective:
-
A typical nuclear power plant generates about 1 GW of power.
-
The total electrical capacity of Germany’s solar PV in 2023 was around 70 GW.
-
The entire electric consumption of a small country might hover around 30-40 GW.
So, 34.9 GW could power:
-
34 nuclear power plants at full capacity.
-
Tens of millions of homes simultaneously.
-
Entire states or small countries for hours or days.
This is not a value you’ll see casually—it’s typically relevant in national energy grids, large-scale renewable energy systems, or high-performance computing infrastructure.
Why Accurate Unit Conversion Matters
1. Engineering and Infrastructure
Engineers must calculate power loads accurately when designing electrical systems. Whether it’s a solar farm or a data center, using the correct unit—watts, kilowatts, or gigawatts—ensures systems are built safely and efficiently.
2. Environmental Analysis
Understanding the scale of energy helps in measuring carbon emissions, energy sustainability, and resource management. Accurate conversions help analysts determine how much renewable energy is needed to replace fossil fuel consumption.
3. Space and Defense Technology
Space agencies and defense sectors use massive amounts of power. Calculating and converting correctly helps mission planning, equipment design, and efficient energy usage in critical operations.
Conversions Made Simple: Formula to Use
Here’s a quick guide you can always use:
To convert watts to gigawatts:
Gigawatts=Watts109\text{Gigawatts} = \frac{\text{Watts}}{10^9}
Or,
GW=W1,000,000,000\text{GW} = \frac{\text{W}}{1,000,000,000}
So:
3.49e10 W=34,900,000,0001,000,000,000=34.9 GW3.49e10 \text{ W} = \frac{34,900,000,000}{1,000,000,000} = 34.9 \text{ GW}
Tools to Help You Convert Watts to Gigawatts
If you’re dealing with such numbers often, consider these tools:
-
Online Unit Converters: Google “watts to gigawatts converter.”
-
Scientific Calculators: Most scientific calculators have an “EXP” or “EE” function for scientific notation.
-
Spreadsheets (like Excel or Google Sheets): Use formulas like
=34900000000/10^9to get instant results.
Use Cases of Gigawatt-Scale Power
⚡ National Power Grids
Countries often measure their total power consumption or generation capacity in gigawatts. For example, the United States may have over 1,200 GW of total electricity capacity.
🔋 Renewable Energy Projects
Gigawatt-scale projects are becoming common in solar and wind energy. China, for instance, has launched ultra-large solar farms generating tens of gigawatts.
🏭 Industrial Power Usage
Large industries like aluminum smelting or semiconductor fabrication plants use power in the gigawatt range due to their high energy needs.
Going Beyond: Other Important Units in Power & Energy
While watts measure the rate of energy use, other units are used to measure energy consumed over time:
-
Watt-hour (Wh): One watt used over an hour.
-
Kilowatt-hour (kWh): Common in household electricity billing.
-
Gigawatt-hour (GWh): Used for large scale electricity production or storage.
-
Terawatt-hour (TWh): Used to measure national or global energy use annually.
So, 34.9 GW sustained over one hour = 34.9 GWh.
Conclusion: From 3.49e10 Watts to a Powerful Perspective
We started with a simple value: 3.49e10 watts. At first glance, it’s just a number. But after converting it into 34.9 gigawatts, we unlock a world of insight. That single number can represent the power of an entire nation’s energy supply, or the ambition behind a massive renewable energy project.
Understanding and mastering these conversions not only sharpens your technical skillset but also gives you a broader appreciation for the forces that drive our technological world—literally.
So, next time you see a number like 3.49e10 W, you’ll know exactly what it means—and why it matters.